Cat coat: what’s the color of your cat?
One question a cat owner often has is: what is the color of my cat? For some, their color can be easily determined, as for black and white cat for example. But for some others it can really be tricky to identify their coat.
Moreover, most cat lovers make the mistake of mixing up colors with breeds, as the siamese for exemple.
Finally, there also are some legends that we all heard of about cat colors. One of these could be : “is it true that all tricolor cats are female ones ?”. In this serie of articles about cat coats, we will answer all of these questions!
Foreword
Before I begin, let me clarify some terms that I am gonna use. The coat of a cat is determined by different things :
the color of the cat ;
the color repartition ;
the pattern ;
tippings ;
...
These components add up together to define the coat of the cat.
Let’s talk about these components.
The first parameter that determine a cat coat is its color. But it certainly is not the only thing that is important.
Second, you have to determine if your cat color is tabby or ‘solid’/’self’. Being tabby means that the cat has some markings and a ‘M’ marking on its face. If a cat is not tabby, then he is said to be ‘solid’ or ‘self’. Those marking we spoke above can be of different kind of pattern. I will speak further about those tabby markings in a specific article.
Third, comes the color repartition. For some cats, the density of color is the same on the whole of its body, but for some others, their extremities can be more colourful or darker. This color repartition is associated to the pointed patterns. A famous example of pointed pattern is the colorpoint pattern which is the one of siamese breed cats. Once more, I will detail everything regarding the different pointed patterns on a following article.
Fourth, are the white spotting. Some cats have white spots on their bodies while others don’t. It will also be detailed in a following article.
Fifth, the cat can have some tippings, meaning that the color is not uniform on the hair. Therefore, only part of the cat hair is colored, which can give some silver reflect to the cat.
Finally there are some other factors which are breed specific and quite rare in house cat to which I will also dedicate some specific articles.
In each article, I will try to keep it simple, but I will add some genetics information for the cat color nerd among us!
At the end of this serie, you will know everything about cat coats.
Coat color
For this first article we will start simple with the base coat color. The coat color can be divided in three categories: the black based colors, the red based colors and white.
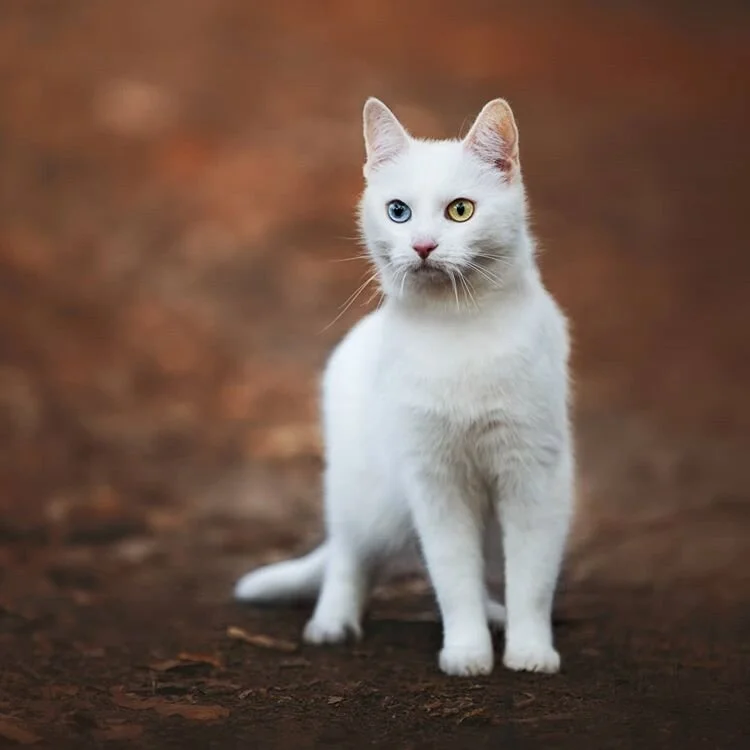
White
Let’s start with the simpler one: white. These cats are entirely white without any markings. Their nose leather and toe beans are pink. The eye color can be blue, green, copper, golden, odd eyed...
White cat from @meowlaska
Red-based colors
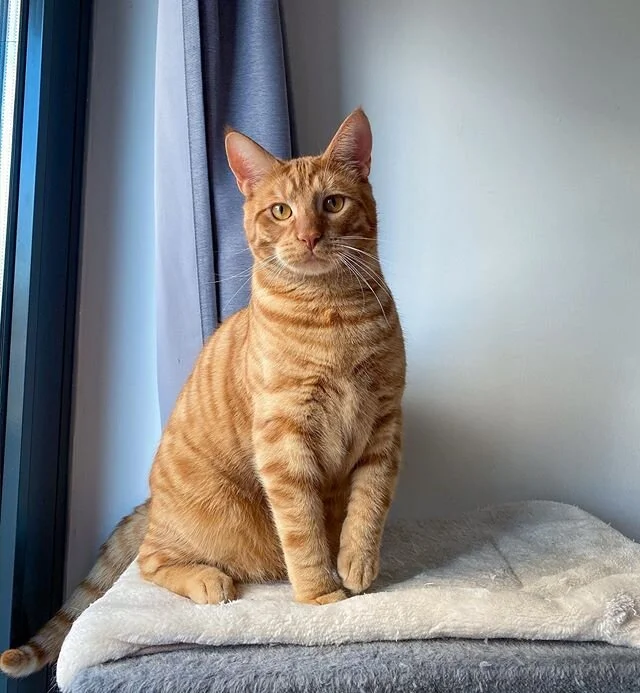
We then have the red based colors: red and cream.
The red colors have many other names, maybe you have heard of ginger, orange, marmalade etc.. It comes in many shades of red from a very warm and deep red to a yellowish color. The nose leather and paw pads are brick red or pink.
Red cat from @cocoandfrits
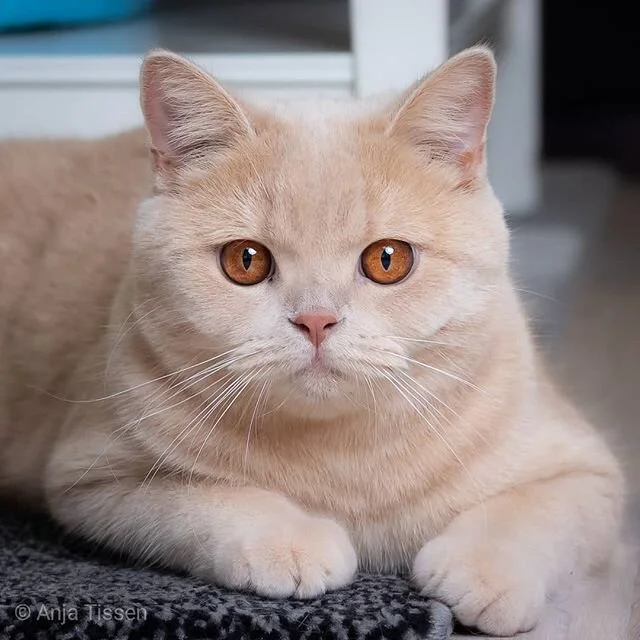
The cream color is a dilution of the red color. The color is pale, with a pastel cream color going from dusty yellow to almost pumpkin. The paw pads and nose leather is pink.
Cream cat from @mr.marlow_bsh
Black based colors
Among black based colors you can find black, blue, chocolate, lilac, cinnamon and fawn.
Blue, lilac and fawn are the dilutions of respectively black, chocolate and cinnamon.
Black
Black is the most common cat color. The fur, nose leather and paw pads are black. Sometimes black cats can appear brownish because of sun discoloration!
Black cat from @woocy_woo
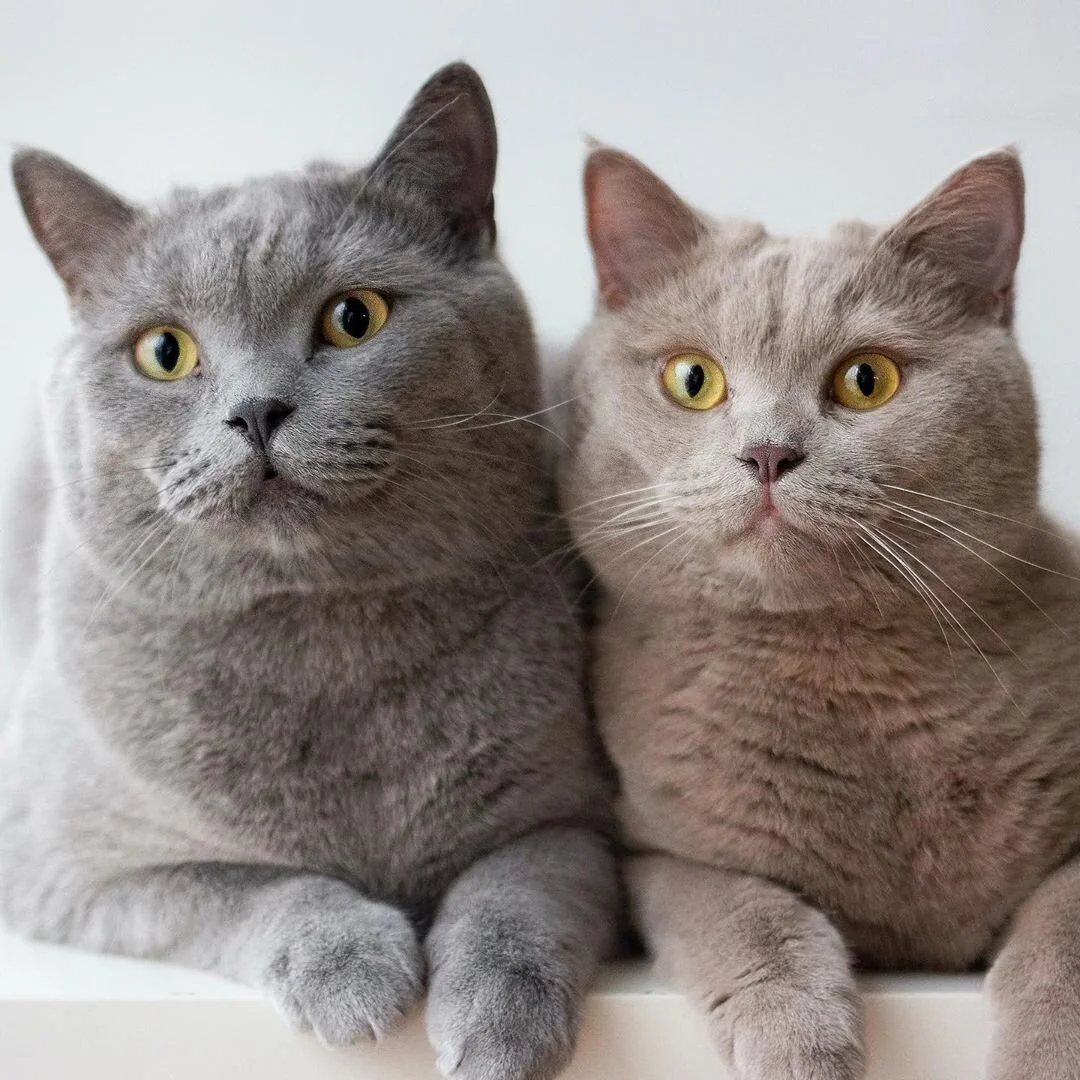
Blue
The blue color is often called grey by cat lovers, it can go from a pale blue-grey to a deep slate grey. The nose leather and paw pads are dark blue or dark grey.
On the left a blue cat and on the right a lilac cat from @lifeofblueoscar
The 4 other colors are rarer among house cats and are mainly found in some cat breeds such as the orientals ones or the british ones.
Chocolate
The cat has a warm dark brown color. The nose leather is chocolate and the paw pads color goes from brown salmon pink to milk-chocolate.
On top: cinnamon cats and on the bottom a chocolate cat from @balinese_javanese_cats
Lilac
A warm lavender color with slightly pinkish tone. The nose leather and paw pads are lavender pink.
Cinnamon
The cat has a warm light brown color, like the color of a cinnamon stick. The nose leather is cinnamon-brown and the paw pads goes from cinnamon brown to pinkish tan. Cinnamon is a lighter chocolate.
Fawn
Warm pinkish beige color, close to the taupe color, the nose leather and paw pads are pinkish fawn. Fawn is a lighter lilac.
Fawn cat from @jasko_nissha
Warning: The lilac and fawn or the chocolate and cinnamon can sometimes be difficult to distinguish from each other, especially in pictures! Depending on the lightning, those colors can easily be confused. A good way to recognize the colors is often to look at the nose leather’s color.
Advanced: Genetics
Some genetics reminder
Each cat have 19 pairs of chromosome. For each pair, one chromosome is coming from the father, and the second one is coming from the mother.
On each chromosome, you find a lot of different genes, that define all of the physical characteristics of the cat. Each genes exist in different versions. And each chromosome of your cat wear of a version of genes. This version is called an allele. As every pair of chromosome is composed of two chromosomes, for every genes your cat got two alleles (version of the gene) : one coming for the mother and the other coming from the father.
If the two alleles are the same, this genes is called homozygous. On the other hand, if the two genes are different, the genes are called heterozygous.
Moreover, an allele can be either dominant (will be written in CAPITAL letter) or recessive. So, let’s imagine we have a gene that is called A (dominant) or a (recessive). The combination held by your cat can be :
AA => the dominant allele will express itself
Aa (or aA) => the dominant allele will express itself
aa => the recessive allele will express itself
As you may see, to express itself, the recessive allele needs to be present on the two chromosomes of the pair. That’s why it is called recessive. On the other hand, as long as the dominant allele is present, it will express itself. And so, you can also understand why the kitten doesn’t always inherit the color of their parents ! Let’s imagine that A is a color and a another color recessive. Now we have the following scenario :
The mother : Aa => its coat color will be A
The father : Aa => its coat color will also be A
Now, during the development of the kittens, those two allele will “separate” from each other and each kitten will get one from each parents. So the kitten can be either :
A(mother)A(father) => color A
A(mother)a(father) => color A
a(mother)A(father) => color A
a(mother)a(father) => color a
And the combination will be different for each kitten ! So now you can understand how it is possible that two cat who are A colored can give birth to an a colored cat. The color allele for a was “hidden” by the dominant allele A.
Let’s now talk about the different colors!
Black
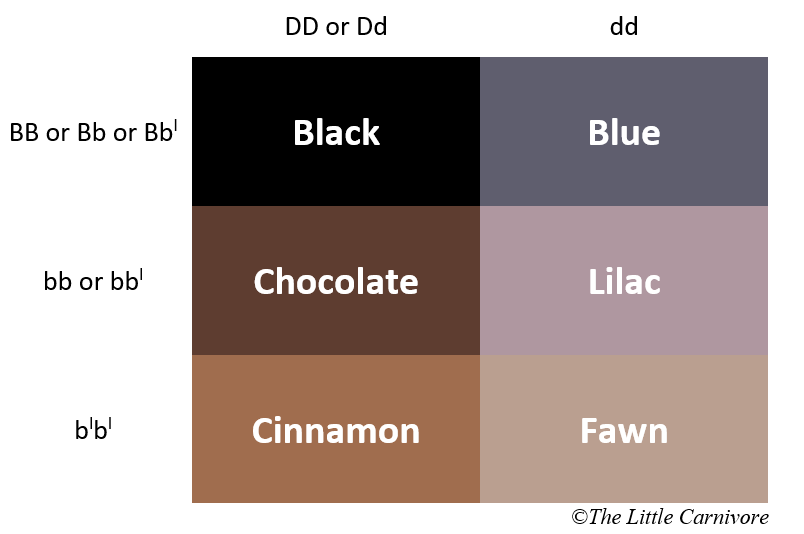
The allele for the black color is noted B and is dominant to the color chocolate noted b and to the color cinnamon noted bl. The chocolate color is itself dominant to the cinnamon. They are all different alleles of the same gene. So if a cat has the alleles BB, Bb or Bbl he will be black, if he has bb or bbl he will be chocolate, and if he has blbl he will be cinnamon.
Dilute
The colors blue, lilac, fawn and cream are called diluted colors. The pigment is not uniformly distributed on their hairs, which gives a lighter and cooler color with sometimes a dusty effect to their coat. The dilute modifier gene being recessive to the non dilute one, the cat has to be homozygous for his coat color to be diluted.
The non-dilute allele is noted D and the dilute is noted d. To have a diluted color the cat must have the allele dd, if the cat is having Dd or DD, he will have a dense coloring.
The dilution is applied to the black or red based color. Blue, lilac, fawn and cream are respectively the dilution of black, chocolate, cinnamon and red.
So for example a fawn cat, which is a diluted cinnamon will be blbl and dd, a lilac cat is bb dd or bbl dd, a cinnamon cat is blbl Dd or blbl DD.
A little summary for black based colors
White
The white color is often called white dominant! In fact, the white gene (W) is dominant to the non white (w). The white gene will also hide the effect of any other color gene of the cat, it's epistatic! So a cat which is BB DD is supposed to be black however if he is carrying Ww or WW, the cat will appear entirely white, if he is ww he will in fact appear black. For reproduction it can be interesting to know which color the white cat is carrying and is hidden by the white!
Red
The genetic of the red color will be detailed in another blog article about the torties, as it’s a sex-linked color and a bit more complex.
Genetic test
The black colors, dilute modifier and white genes can all be tested, meaning that with a DNA test you can determine the two alleles of your cats. This can be useful for some colors like lilac or fawn which can sometime be difficult to identify, or to know which recessive gene a cat is carrying. For example, by looking at a black cat you don’t know if he is heterozygous: carrying the gene for chocolate or cinnamon (meaning that he is Bb or Bbl) or if he is homozygous (BB). This can sometimes be guessed if you know the color of the parents, in other cases it can only be determined by a genetic test.
When you breed two cats, the kitten will randomly get one allele from each parent. If you know the alleles of the parents, you can determine the different color possibilities of the kittens.
Here are all the base colors of cats. In the next article we will talk about the red and tortie cats, so stay tuned to know more about cat furs!
Source
Fifé
TICA
LOOF
Messy Beast
Helorimer
Other article on cat coat
Torties and red cats
Tabby cats
Point colorations
White cats and white spotting
Silver and smoke cats